StrutStyle class
Defines the strut, which sets the minimum height a line can be relative to the baseline.
Strut applies to all lines in the paragraph. Strut is a feature that allows minimum line heights to be set. The effect is as if a zero width space was included at the beginning of each line in the paragraph. This imaginary space is 'shaped' according the properties defined in this class. Flutter's strut is based on typesetting strut and CSS's line-height.
No lines may be shorter than the strut. The ascent and descent of the strut are calculated, and any laid out text that has a shorter ascent or descent than the strut's ascent or descent will take the ascent and descent of the strut. Text with ascents or descents larger than the strut's ascent or descent will layout as normal and extend past the strut.
Strut is defined independently from any text content or TextStyles.
The vertical components of strut are as follows:
- Half the font-defined leading
ascent * heightdescent * height- Half the font-defined leading
The sum of these four values is the total height of the line.
Ascent is the font's spacing above the baseline without leading and
descent is the spacing below the baseline without leading. Leading is
split evenly between the top and bottom. The values for ascent and
descent are provided by the font named by fontFamily. If no
fontFamily or fontFamilyFallback is provided, then the platform's
default family will be used. Many fonts will have leading values of
zero, so in practice, the leading component is often irrelevant.
When height is omitted or null, then the font defined ascent and descent
will be used. The font's combined ascent and descent may be taller or
shorter than the fontSize. When height is provided, the line's EM-square
ascent and descent (which sums to fontSize) will be scaled by height to
achieve a final line height of fontSize * height + fontSize * leading
logical pixels. The proportion of ascent:descent with height specified
is the same as the font metrics defined ascent:descent ratio.

Each line's spacing above the baseline will be at least as tall as the half leading plus ascent. Each line's spacing below the baseline will be at least as tall as the half leading plus descent.
See also:
- StrutStyle, the class in the dart:ui library.
Fields and their default values.
Omitted or null properties will take the default values specified below:
-
fontFamily: the name of the font to use when calculating the strut (e.g., Roboto). No glyphs from the font will be drawn and the font will be used purely for metrics.
-
fontFamilyFallback: an ordered list of font family names that will be searched for when the font in fontFamily cannot be found. When all specified font families have been exhausted an no match was found, the default platform font will be used.
-
fontSize: the size of the ascent plus descent in logical pixels. This is also used as the basis of the custom leading calculation. This value cannot be negative. Default is 14 logical pixels.
-
height: the multiple of fontSize the line's height should be. The line's height will take the font's ascent and descent values if height is omitted or null. If provided, the EM-square ascent and descent (which sum to fontSize) is scaled by height. The height will impact the spacing above and below the baseline differently depending on the ratios between the font's ascent and descent. This property is separate from the leading multiplier, which is controlled through leading. Default is null.
-
leading: the custom leading to apply to the strut as a multiple of fontSize. Leading is additional spacing between lines. Half of the leading is added to the top and the other half to the bottom of the line height. This differs from height since the spacing is equally distributed above and below the baseline. Default is null, which will use the font-specified leading.
-
fontWeight: the typeface thickness to use when calculating the strut (e.g., bold). Default is FontWeight.w400.
-
fontStyle: the typeface variant to use when calculating the strut (e.g., italic). Default is FontStyle.normal.
-
forceStrutHeight: when true, all lines will be laid out with the height of the strut. All line and run-specific metrics will be ignored/overridden and only strut metrics will be used instead. This property guarantees uniform line spacing, however text in adjacent lines may overlap. This property should be enabled with caution as it bypasses a large portion of the vertical layout system. The default value is false.
Examples
const Text(
'Hello, world!\nSecond line!',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 10,
fontFamily: 'Raleway',
),
strutStyle: StrutStyle(
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
fontSize: 30,
height: 1.5,
),
)Second line! without
causing the line height to change for the second line only. All lines in
this example are thus the same height (14 * 1.5).
const Text.rich(
TextSpan(
text: 'First line!\n',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: 'Roboto'
),
children: <TextSpan>[
TextSpan(
text: 'Second line!\n',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 16,
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
),
),
TextSpan(
text: 'Third line!\n',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
),
),
],
),
strutStyle: StrutStyle(
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
height: 1.5,
),
)Ms in lines 2 and 3 are able to extend above their lines and
fill empty space in lines above. The forceStrutHeight is enabled and functions
as a 'grid' for the glyphs to draw on.
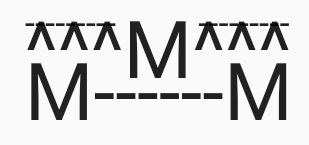
const Text.rich(
TextSpan(
text: '--------- ---------\n',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
),
children: <TextSpan>[
TextSpan(
text: '^^^M^^^\n',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 30,
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
),
),
TextSpan(
text: 'M------M\n',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 30,
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
),
),
],
),
strutStyle: StrutStyle(
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
fontSize: 14,
height: 1,
forceStrutHeight: true,
),
)
const Text.rich(
TextSpan(
text: ' he candle flickered\n',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: 'Serif'
),
children: <TextSpan>[
TextSpan(
text: 'T',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 37,
fontFamily: 'Serif'
),
),
TextSpan(
text: 'in the moonlight as\n',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: 'Serif'
),
),
TextSpan(
text: 'Dash the bird fluttered\n',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: 'Serif'
),
),
TextSpan(
text: 'off into the distance.',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: 'Serif'
),
),
],
),
strutStyle: StrutStyle(
fontFamily: 'Serif',
fontSize: 14,
forceStrutHeight: true,
),
)- Mixed-in types
- Annotations
Constructors
-
StrutStyle({String? fontFamily, List<
String> ? fontFamilyFallback, double? fontSize, double? height, TextLeadingDistribution? leadingDistribution, double? leading, FontWeight? fontWeight, FontStyle? fontStyle, bool? forceStrutHeight, String? debugLabel, String? package}) -
Creates a strut style.
const
-
StrutStyle.fromTextStyle(TextStyle textStyle, {String? fontFamily, List<
String> ? fontFamilyFallback, double? fontSize, double? height, TextLeadingDistribution? leadingDistribution, double? leading, FontWeight? fontWeight, FontStyle? fontStyle, bool? forceStrutHeight, String? debugLabel, String? package}) -
Builds a StrutStyle that contains values of the equivalent properties in
the provided
textStyle.
Properties
- debugLabel → String?
-
A human-readable description of this strut style.
final
- fontFamily → String?
-
The name of the font to use when calculating the strut (e.g., Roboto). If
the font is defined in a package, this will be prefixed with
'packages/package_name/' (e.g. 'packages/cool_fonts/Roboto'). The
prefixing is done by the constructor when the
packageargument is provided.final -
fontFamilyFallback
→ List<
String> ? -
The ordered list of font families to fall back on when a higher priority
font family cannot be found.
no setter
- fontSize → double?
-
The size of text (in logical pixels) to use when obtaining metrics from the font.
final
- fontStyle → FontStyle?
-
The typeface variant to use when calculating the strut (e.g., italics).
final
- fontWeight → FontWeight?
-
The typeface thickness to use when calculating the strut (e.g., bold).
final
- forceStrutHeight → bool?
-
Whether the strut height should be forced.
final
- hashCode → int
-
The hash code for this object.
no setteroverride
- height → double?
-
The minimum height of the strut, as a multiple of fontSize.
final
- leading → double?
-
The additional leading to apply to the strut as a multiple of fontSize,
independent of height and leadingDistribution.
final
- leadingDistribution → TextLeadingDistribution?
-
How the vertical space added by the height multiplier should be
distributed over and under the strut.
final
- runtimeType → Type
-
A representation of the runtime type of the object.
no setterinherited
Methods
-
compareTo(
StrutStyle other) → RenderComparison - Describe the difference between this style and another, in terms of how much damage it will make to the rendering.
-
debugFillProperties(
DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties, {String prefix = ''}) → void -
Adds all properties prefixing property names with the optional
prefix.override -
inheritFromTextStyle(
TextStyle? other) → StrutStyle -
Returns a new strut style that inherits its null values from
corresponding properties in the
otherTextStyle. -
merge(
StrutStyle? other) → StrutStyle -
Returns a new strut style that is a combination of this style and the given
otherstyle. -
noSuchMethod(
Invocation invocation) → dynamic -
Invoked when a nonexistent method or property is accessed.
inherited
-
toDiagnosticsNode(
{String? name, DiagnosticsTreeStyle? style}) → DiagnosticsNode -
Returns a debug representation of the object that is used by debugging
tools and by DiagnosticsNode.toStringDeep.
inherited
-
toString(
{DiagnosticLevel minLevel = DiagnosticLevel.info}) → String -
A string representation of this object.
inherited
-
toStringShort(
) → String -
A brief description of this object, usually just the runtimeType and the
hashCode.
override
Operators
-
operator ==(
Object other) → bool -
The equality operator.
override
Constants
- disabled → const StrutStyle
- A StrutStyle that will have no impact on the text layout.